Publications
Selected
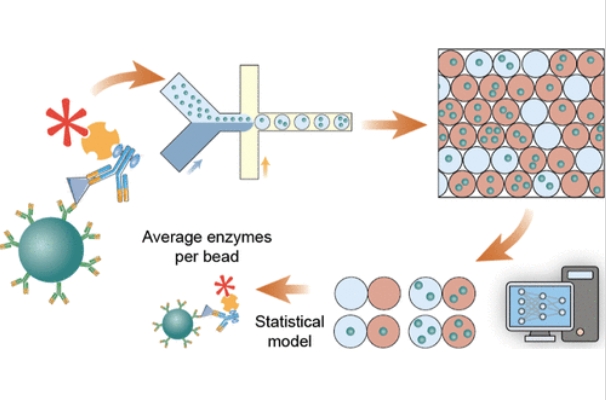
This study introduces a new type of ultra-sensitive protein detection method called inclusive droplet digital ELISA (iddELISA). Unlike traditional digital tests that only use droplets with one bead, this method uses all droplets—even those with multiple beads—by applying a smart statistical model. This improves both the efficiency and accuracy of detection. Demonstrated with COVID-19 nucleocapsid protein, the new method achieved detection limits far lower than existing techniques. This innovation could help in early disease diagnosis where protein levels are extremely low.
Yujuan Chai, Xiaoxiang Hu, Qi Fang, Yuanyuan Guo, Binmao Zhang, Hangjia Tu, and Zida Li*
Anal. Chem. 97(1), 444–453 (2025)
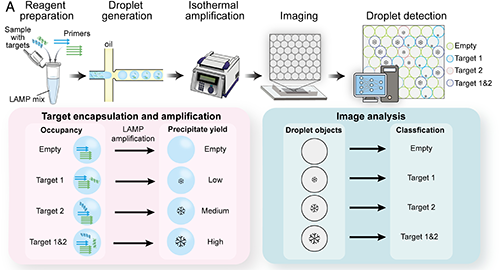
We developed StratoLAMP, a new method for detecting multiple genetic targets without the need for complex or costly fluorescent labels. Instead, we use a natural byproduct from a common DNA amplification reaction—tiny particles that form during the process—as a visual signal. By carefully designing the system, we can tell which genes are present just by looking at the amount of these particles in each droplet. We then use AI-powered image analysis to interpret the results with high accuracy. StratoLAMP makes genetic testing simpler, more affordable, and better suited for use outside of high-tech labs—an exciting step toward more accessible diagnostics.
Meichi Jin,# Jingyi Ding,# Yu Zhou, Jiazhao Chen, Yi Wang, and Zida Li*
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 121(2), e2314030121, (2024)
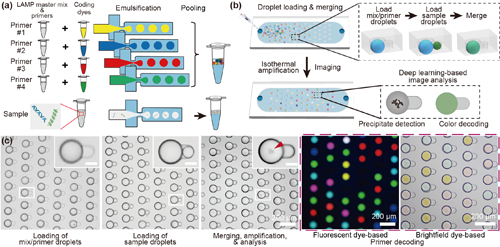
This paper introduces CoID-LAMP, a new method for detecting and measuring multiple genetic materials (nucleic acids) simultaneously. Instead of using complicated fluorescent tags for each target, CoID-LAMP uses simple colored droplets and deep learning image analysis to identify and count different genetic targets. The system pairs color-coded primer droplets with sample droplets on a small chip, allowing the reaction to take place and be observed with basic imaging tools. The method works accurately with both fluorescent and non-fluorescent (brightfield) dyes, making it low-cost and user-friendly. This technology could help make genetic testing faster, easier, and more accessible.
Kai Wu,# Qi Fang,# Zhantao Zhao, and Zida Li*
Anal. Chem. 95(11), 5069–5078 (2023)
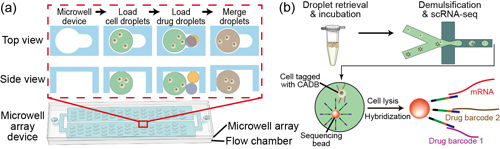
This study introduces a new technology called CP-seq, which helps researchers test combinations of drugs on individual cells. It works by tagging each drug with a unique barcode and using microfluidic devices to randomly mix drugs with cells in tiny droplets. After treatment, scientists can read both the cell’s genetic response and the drug combination it received. This method allows thousands of drug combinations to be tested quickly and efficiently, offering a powerful tool for discovering better treatments and reducing drug resistance.
Run Xie,# Yang Liu,# Shiyu Wang, Xuyang Shi, Zhantao Zhao, Longqi Liu, Ya Liu,* and Zida Li*
Biosens. Bioelectron. 220, 114913 (2023)
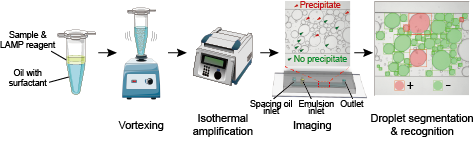
This study introduces “deep-dLAMP,” a low-cost method for quantifying nucleic acids using common lab equipment and advanced deep learning. Instead of requiring expensive tools to create uniform droplets, the method uses simple vortex mixing to produce droplets of various sizes and applies deep learning to analyze images of these droplets. It identifies whether each droplet contains a DNA amplification product by detecting visible precipitates, and then calculates the DNA concentration based on droplet size and occupancy using statistical models. This method is accurate, robust across different conditions, and has the potential to be widely used in labs or point-of-care testing.
Linzhe Chen,# Jingyi Ding,# Hao Yuan, Chi Chen,* and Zida Li*
Adv. Sci. 9(9), 2105450 (2022)
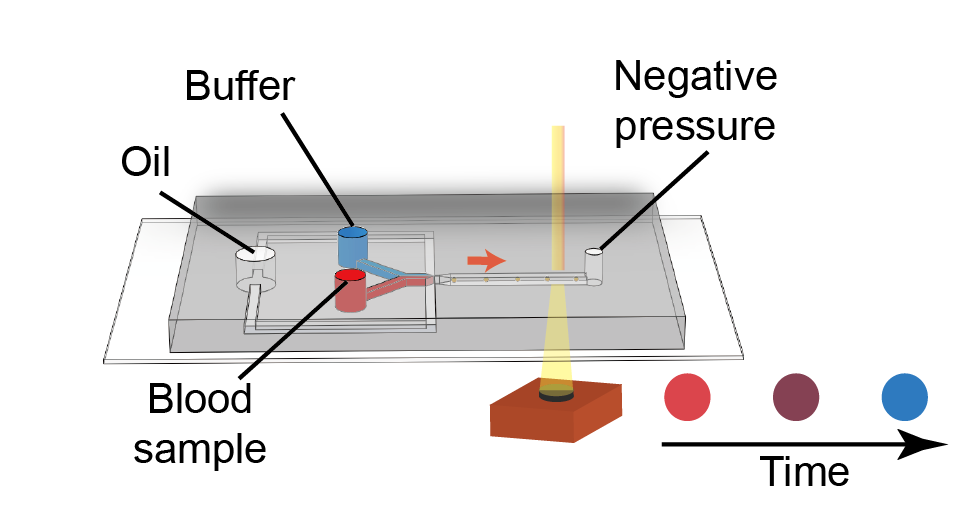
This study presents a new, easy-to-use blood testing device that measures how quickly blood clots, which is important for surgeries and managing certain diseases. The device works by mixing blood with a buffer in tiny droplets and tracking how the color of these droplets changes as the blood becomes thicker (more viscous). By analyzing the droplet colors, the system can determine the blood’s clotting behavior. The researchers also built a simple, portable version of the device, showing that it could be used outside traditional labs, such as in clinics or emergency situations.
Linzhe Chen, Donghao Li, Xinyu Liu, Yihan Xie, Jieying Shan, Haofan Huang, Xiaxia Yu, Yudan Chen, Weidong Zheng, and Zida Li*
ACS Sens. 7(8), 2170–2177 (2022)
Full List of Publications
2026
AI-Guided Droplet Microreactors Enable Rapid and Reproducible Protein Crystallization
Guangzhu Shang, Peiyi Zheng, Hengzhi Ni, Shan Wei, Luoquan Li, Xingyue Lei, Zerui Wu, Xiaogang He, Zirui Wang, Zhongliang Zhu, Huichao Ou, Liqun He,* Zida Li,* Tengchuan Jin,* and Gang Zhao*
Small, in press (2026)
2025
Flow-LAMP: Label-free Digital LAMP using Scatter-based Flow Cytometry on Vortex-Generated Polydisperse Gel Beads
Yuchong Zheng, Wanjun Yao, Zerui Wu, Liqun He, Weidong Zheng,* and Zida Li*
Analytical Chemistry, 97(41), 22878–22886 (2025)
StratoLAMP-2: A Microfluidics-Free, Deep-Learning Platform for Multiplex Digital Molecular Diagnostics
Jiazhao Chen,# Jingyi Ding,# Rui Deng, Yi Wang,* and Zida Li*
Analytical Chemistry, 97(40), 22259–22269 (2025)
From Droplets to Diagnosis: AI-Driven Imaging and System Integration in Digital Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing
Yuanyuan Wei, Xianxian Liu, Yao Mu, Changran Xu, Guoxun Zhang, Tianhao Li, Zida Li, Wu Yuan,* Ho-Pui Ho,* and Mingkun Xu*
Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 288, 117741 (2025)
Materials-Driven Innovations in Digital Nucleic Acid Amplification Technologies: Transforming Molecular Diagnostics
Jiazhao Chen, Kai Wu, Jingyi Ding, and Zida Li*
Chemical Engineering Journal, 519, 165127 (2025)
Reimagining POCT assays: Automated digital microfluidics for multiplex in vitro diagnostics
Wenkai Fan, Donghao Li, Jingyi Ding, and Zida Li*
Talanta, 294, 128270 (2025)
Droplet digital PCR-based single aptamer selection
Zerui Wu,# Wanjun Yao,# Jinyu Chen, Yonghao Chen, Zida Li, Weiping Ding,* Liqun He,* and Peng Hu*
Talanta, 127924 (2025)
Embracing Poisson encapsulation statistics for improved droplet digital immunoassay
Yujuan Chai, Xiaoxiang Hu, Qi Fang, Yuanyuan Guo, Binmao Zhang, Hangjia Tu, and Zida Li*
Anal. Chem. 97(1), 444–453 (2025)
2024
StratoLAMP: Label-free, multiplex digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification based on visual stratification of precipitate
Meichi Jin,# Jingyi Ding,# Yu Zhou, Jiazhao Chen, Yi Wang, and Zida Li*
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 121(2), e2314030121, (2024)
Image-activated pico-injection for single cell analysis
Zhantao Zhao, Heng Zhai, Peng Zuo, Tao Wang, Run Xie, Mu Tian, Ruyuan Song, Xiaonan Xu, and Zida Li*
Talanta 272, 125765 (2024)
2023
CoID-LAMP: Color-encoded, intelligent digital LAMP for multiplexed nucleic acid quantification
Kai Wu,# Qi Fang,# Zhantao Zhao, and Zida Li*
Anal. Chem. 95(11), 5069–5078 (2023)
Combinatorial perturbation sequencing on single cells using microwell-based droplet random pairing
Run Xie,# Yang Liu,# Shiyu Wang, Xuyang Shi, Zhantao Zhao, Longqi Liu, Ya Liu,* and Zida Li*
Biosens. Bioelectron. 220, 114913 (2023)
High resolution, multiplex antibody patterning using micropillar-focused droplet printing and microcontact printing
Meichi Jin, Kai Wu, Mengzhen Wang, Yang Zhang, Chengbin Yang, and Zida Li*
Adv. Biol. 7(8), 2300111 (2023)
Bone-on-a-chip platforms and integrated biosensors: towards advanced in vitro bone models with real-time biosensing
Yang Zhang, Taozhao Yu, Jingyi Ding, and Zida Li*
Biosens. Bioelectron. 219, 114798 (2023)
2022
deep-dLAMP: deep learning-enabled polydisperse emulsion-based digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Linzhe Chen,# Jingyi Ding,# Hao Yuan, Chi Chen,* and Zida Li*
Adv. Sci. 9(9), 2105450 (2022)
Point-of-care blood coagulation assay based on dynamic monitoring of blood viscosity using droplet microfluidics
Linzhe Chen, Donghao Li, Xinyu Liu, Yihan Xie, Jieying Shan, Haofan Huang, Xiaxia Yu, Yudan Chen, Weidong Zheng, and Zida Li*
ACS Sens. 7(8), 2170–2177 (2022)
Generation and Screening of Antigen-Specific Nanobodies from Mammalian Cells Expressing the BCR Repertoire Library Using Droplet-Based Microfluidics
Menghua Lyu,# Xuyang Shi,# Xiaopan Liu,# Yang Liu, Xijun Zhu, Lijuan Liao, Hongyan Zhao, Na Sun, Shiyu Wang, Linzhe Chen, Linyuan Fan, Qumiao Xu, Qianqian Zhu, Kai Gao, Huaying Chen, Yonggang Zhu, Zida Li, Weijin Guo, Yue Zheng, Ying Gu, Longqi Liu,* Meiniang Wang,* and Ya Liu*
Anal. Chem. 94(22), 7970–7980 (2022)
Point-of-care blood coagulation assay enabled by printed circuit board-based digital microfluidics
Donghao Li,# Xinyu Liu,# Yujuan Chai,# Jieying Shan, Yihan Xie, Yong Liang, Susu Huang, Weidong Zheng, and Zida Li*
Lab Chip 22(4), 709-716 (2022)
Single-cell sequencing to unveil the mystery of embryonic development
Zida Li,#,* Feng Lin,# Chu-Han Zhong, Shue Wang, Xufeng Xue, and Yue Shao*
Adv. Biol. 6(2), 2101151 (2022)
High-throughput functional screening of antigen-specific T-cells based on droplet microfluidics on single-cell level
Shiyu Wang,# Yang Liu,# Yijian Li, Menghua Lv, Kai Gao, Ying He, Wenbo Wei, Yonggang Zhu, Xuan Dong, Xun Xu, Zida Li,* Longqi Liu,* and Ya Liu*
Anal. Chem. 94(2), 918–926 (2022)
2021
Emerging biosensing technologies for improved diagnostics of COVID-19 and future pandemics
Linzhe Chen, Guoliang Zhang, Longqi Liu, and Zida Li
Talanta 225, 121986 (2021)
2020
Micro-engineered flexural post rings for effective blood sample fencing and high throughput measurement of clot retraction force
Lanzhu Huang,# Xinyu Liu,# Yuanbin Ou, Haofan Huang, Xia Zhang, Yize Wang, Yong Liang, Xiaxia Yu, Weidong Zheng, Huisheng Zhang, and Zida Li*
ACS Sens. 5(12), 3949-3955 (2020)
Recent advances in solar-driven evaporation system
Zhourui Xu, Zida Li, Yihang Jiang, Gaixia Xu, Mingwei Zhu, Wing-Cheung Law, Ken-Tye Yong, Yanshuai Wang, Chengbin Yang, Biqin Dong, and Feng Xing*
J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 25571-25600 (2020)
Stretchable supercapacitors as emergent energy storage units for health monitoring bioelectronics
Xue Chen, Nicolo Simone Villa, Yanfeng Zhuang, Linzhe Chen, Tianfu Wang, Zida Li, and Tiantian Kong
Adv. Energy Mater. 10(4), 1902769 (2020)
2019
Dean flow assisted single cell and bead encapsulation for high performance single cell expression profiling
Luoquan Li,# Ping Wu,# Zhaofeng Luo, Lei Wang, Weiping Ding, Tao Wu, Jinyu Chen, Jinlong He, Yi He, Heran Wang, Ying Chen, Guibo Li, Zida Li,* and Liqun He*
ACS Sens. 4(5), 1299-1305 (2019)
Multiple splitting of droplets using multi-furcating microfluidic channels
Zida Li, Luoquan Li, Meixiang Liao, Liqun He, and Ping Wu
Biomicrofluidics 13(2), 024112 (2019)
Controlled modeling of human epiblast and amnion development using stem cells
Yi Zheng, Xufeng Xue, Yue Shao, Sicong Wang, Sajedeh Nasr Esfahani, Zida Li, Jonathon M. Muncie, Johnathon N. Lakins, Valerie M. Weaver, Deborah L. Gumucio, and Jianping Fu*
Nature 573(7774), 421-425 (2019)
Dorsal-ventral patterned neural cyst from human pluripotent stem cells in a neurogenic niche
Yuanyuan Zheng,# Xufeng Xue,# Agnes M. Resto Irizarry, Zida Li, Yue Shao, Yi Zheng, Gang Zhao,* and Jianping Fu*
Sci. Adv. 5(12), eaax5993 (2019)
Microengineered human amniotic ectoderm tissue array for high-content developmental phenotyping
Sajedeh Nasr Esfahani, Yue Shao, Agnes M Resto Irizarry, Zida Li, Xufeng Xue, Deborah L Gumucio, and Jianping Fu*
Biomaterials 216, 119244 (2019)
Biophysical phenotypes and determinants of anterior vs. posterior primitive streak cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells
Feng Lin, Yue Shao, Xufeng Xue, Yi Zheng, Zida Li, Chunyang Xiong, and Jianping Fu
Acta Biomater. 86, 125-134 (2019)
2018 and earlier
Carbon nanotube strain sensor based hemoretractometer for blood coagulation testing
Zida Li, Yize Wang, Xufeng Xue, Brendan McCracken, Kevin Ward, and Jianping Fu*
ACS Sens. 3(3), 670-676 (2018)
Capillary assisted deposition of carbon nanotube film for strain sensing
Zida Li, Xufeng Xue, Feng Lin, Yize Wang, Kevin Ward, and Jianping Fu*
Appl. Phys. Lett. 111(17), 173105 (2017)
Tracking the tumor invasion front using long-term fluidic tumoroid culture
Koh Meng Aw Yong, Zida Li, Sofia D. Merajver, and Jianping Fu*
Sci. Rep. 7, (2017)
Acoustic tweezing cytometry enhances osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through cytoskeletal contractility and YAP activation
Xuefeng Xue, Xiaowei Hong, Zida Li, Cheri X. Deng, and Jianping Fu*
Biomaterials 134, 22-30 (2017)
Controlled tubular unit formation from collagen film for modular tissue engineering
Jianming Sang, Xiang Li, Yue Shao, Zida Li, and Jianping Fu*
ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 3(11), 2860-2868 (2016)
A miniaturized hemoretractometer for blood clot retraction testing
Zida Li, Xiang Li, Brendan McCracken, Yue Shao, Kevin Ward, and Jianping Fu*
Small 12, 3926–3934 (2016)
Musical interfaces: visualization and reconstruction of music with a microfluidic two-phase flow
Sze Yi Mak, Zida Li, Arnaud Frere, Tat Chuen Chan, and Ho Cheung Shum*
Sci. Rep. 4, 6675 (2014)
Syringe-pump-induced fluctuation in all-aqueous microfluidic system implications for flow rate accuracy
Zida Li, Sze Yi Mak, Alban Sauret, and Ho Cheung Shum*
Lab Chip 14(4), 744-749 (2014)
Emerging microengineered tools for functional analysis and phenotyping of blood cells
Xiang Li, Weiqiang Chen, Zida Li, Ling Li, Hongchen Gu, and Jianping Fu*
Trends Biotechnol. 32(11), 586-594 (2014)
Dynamics for dense packing of colloids
Liqun He*, Ping Wu, Zida Li, and Lili Feng
Adv. Mater. Res. 165, 248-254 (2012)
Patents
Zida Li, Tao Wang, Yongjin Zhou, Zengtong Chen
A system and method for single cell isolation using droplet microfluidics
China Invention Patent Provisional Application, CN113477282A (2021)
Zida Li, Jingyi Ding, Linzhe Chen, Chi Chen
A nucleic acid quantification method based on non-uniform droplets and image analysis
China Invention Patent Provisional Application, CN114540469A (2022)
Zida Li, Qi Fang, Yujun Chai, Xiaoxiang Hu
A Droplet Digital Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Method, Device, and Related Medium
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202410149722.7 (2024)
Zida Li, Donghao Li, Yujuan Chai, Xinyu Liu, Weidong Zheng
A detection system and method for point-of-care blood clotting function assessment
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202111620552.9 (2025)
Zida Li, Linzhe Chen, Weidong Zheng, Jieying Shan, Yihan Xie, Xinyu Liu
A device and method for the assessement of blood viscosity using microfluidics
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202110639057.6 (2021)
Zida Li, Meichi Jin, Jingyi Ding, Yi Wang, Yu Zhou
The Multiplex Nucleic Acid Quantification Method, Device, and Medium Based on Precipitation Bright Field Image Processing
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202310028332.X (2022)
Zida Li, Zhantao Zhao
An image-activated picoinjection method, system, and equipment
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202211449260.8 (2023)
Zida Li, Qi Fang, Kai Wu
Method, device, and medium for multiple digital detection of nucleic acid with deep learning
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202211516857.X (2023)
Zida Li, Xiaxia Yu, Xinyu Liu, Jieying Shan, Yihan Xie
Simulation system and method of in vitro diagnostics
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202110750662.0 (2023)
Zida Li, Lanzhu Huang, Weidong Zheng
A fabrication method and application of soft post rings for clot retraction testing
China Invention Patent Application, ZL202010260648.8 (2022)
Jianping Fu, Kevin Ward, Zida Li, Xiang Li
A microscale device for blood coagulation assay
U.S. Patent Application, 62/304,385 (2018)
Ho Cheung Shum, Alban Sauret, Zida Li, Yang Song
System and method for generation of emulsions with low interfacial tension and measuring frequency vibrations in the system
U.S. Patent Application, 13/839,072 (2013)