Our research is focused on addressing problems in biomedical research using our expertise in micro-/nano-technology. We are particularly interested in
- Single-molecule analysis of nucleic acids
- Single-cell analysis
- Blood coagulation testing
- Miscellaneous microfluidic tools
Some of the past and ongoing projects are shown below. Available facilities are shown here.
Single-molecule analysis of nucleic acids
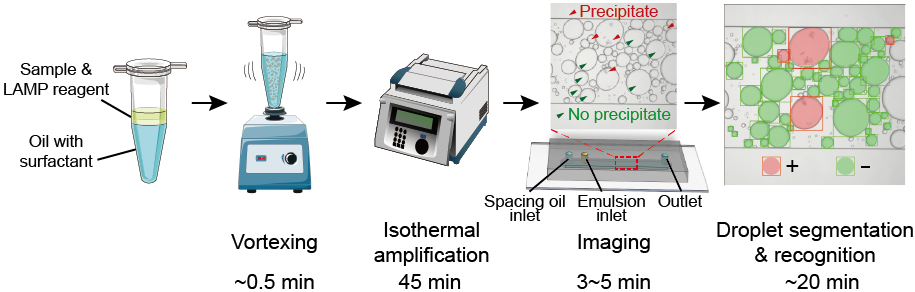
Nucleic acid detection plays a central role in the identification of pathogen infection, diagnosis of genetic diseases, and genetic analysis. The commonly used method of real-time PCR requires references for quantification. In contrast, the emerging technology of digital PCR offers a means for absolute quantification. However, existing digital PCR technical platforms require sophisticated instruments for compartmentalization and signal reading, limiting their widespread applications. In addition, only a handful of nucleic acid targets can be simultaneously tested. In our lab, we aim to develop low cost, portable, multiplex methods for digital nucleic acid tests using microfluidic tools and machine learning algorithms.
Relevant Publications:
- StratoLAMP: Label-free, multiplex digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification based on visual stratification of precipitate
Meichi Jin,# Jingyi Ding,# Yu Zhou, Jiazhao Chen, Yi Wang, and Zida Li*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
, 121(2), e2314030121, 2024
DOI | PDF - deep-dLAMP: deep learning-enabled polydisperse emulsion-based digital loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Linzhe Chen,# Jingyi Ding,# Hao Yuan, Chi Chen,* and Zida Li*
Advanced Science
, 9(9), 2105450, 2022
DOI | PDF - CoID-LAMP: Color-encoded, intelligent digital LAMP for multiplexed nucleic acid quantification
Kai Wu,# Qi Fang,# Zhantao Zhao, and Zida Li*
Analytical Chemistry
, 95(11), 5069–5078, 2023
DOI | PDF
Single-cell analysis
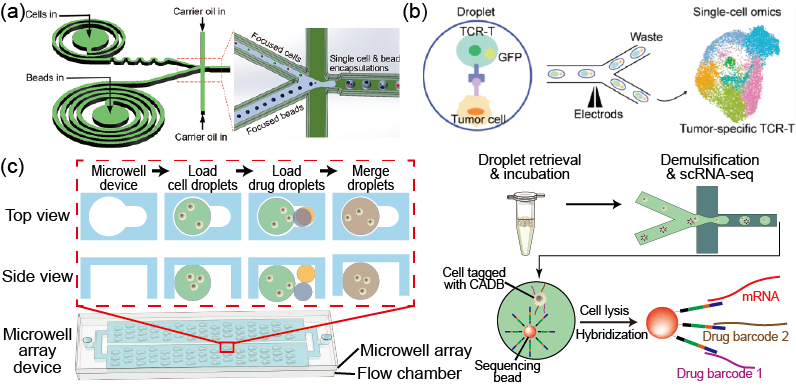
Every cell is special. Bulk analysis takes ensemble average of the biological samples, while single cell analysis offers the opportunity to tease out cell heterogeneity. A typical pipeline of single cell analysis including cell isolation, library construction, sequencing, and stats, and droplet microfluidics offers a method to isolate and process cells with ultrahigh throughput. We are currently working on improving the performance of droplet microfluidics in single cell analysis, in terms of cell encapsulation, droplet sorting, and barcoding. We work closely with our collaborators in sequencing industry.
Relevant Publications:
- Image-activated pico-injection for single cell analysis
Zhantao Zhao, Heng Zhai, Peng Zuo, Tao Wang, Run Xie, Mu Tian, Ruyuan Song, Xiaonan Xu, and Zida Li*
Talanta
, 272, 125765, 2024
DOI | PDF - Combinatorial perturbation sequencing on single cells using microwell-based droplet random pairing
Run Xie,# Yang Liu,# Shiyu Wang, Xuyang Shi, Zhantao Zhao, Longqi Liu, Ya Liu,* and Zida Li*
Biosensors and Bioelectronics
, 220, 114913, 2023
DOI | PDF - High-throughput functional screening of antigen-specific T-cells based on droplet microfluidics on single-cell level
Shiyu Wang,# Yang Liu,# Yijian Li, Menghua Lv, Kai Gao, Ying He, Wenbo Wei, Yonggang Zhu, Xuan Dong, Xun Xu, Zida Li*, Longqi Liu*, and Ya Liu*
Analytical Chemistry
, 94(2), 918–926, 2022
DOI | PDF
Blood coagulation assay
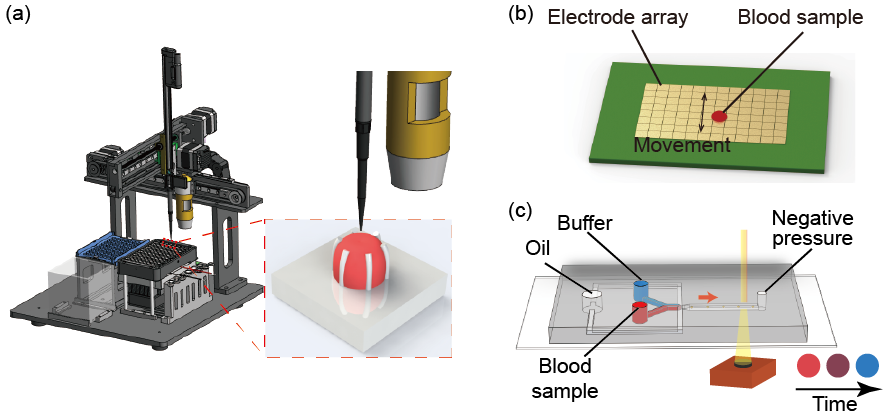
Monitoring of coagulation function has applications in many clinical settings, but routine coagulation assays are sample-consuming and slow in turnaround. In our lab, we leverage the advantage of microfluidics in developing miniaturized assays and develop novel coagulation assays that are applicable in point-of-care settings. Specifically, we develop microfluidic sensors that assess the mechanical properties, namely clot retraction force and viscosity, of the blood during clotting.
Relevant Publications:
- Point-of-care blood coagulation assay enabled by printed circuit board-based digital microfluidics
Donghao Li#, Xinyu Liu#, Yujuan Chai#, Jieying Shan, Yihan Xie, Yong Liang, Susu Huang, Weidong Zheng, and Zida Li*
Lab on a Chip
, 22(4), 709-716, 2022
DOI | PDF - Micro-engineered flexural post rings for effective blood sample fencing and high throughput measurement of clot retraction force
Lanzhu Huang#, Xinyu Liu#, Yuanbin Ou, Haofan Huang, Xia Zhang, Yize Wang, Yong Liang, Xiaxia Yu, Weidong Zheng, Huisheng Zhang, and Zida Li*
ACS Sensors
, 5(12), 3949-3955, 2020
DOI | PDF - A miniaturized hemoretractometer for blood clot retraction testing
Zida Li, Xiang Li, Brendan McCracken, Yue Shao, Kevin Ward, and Jianping Fu*
Small
, 12, 3926–3934, 2016
DOI | PDF
Microfluidic tools

In our lab, we are also interested in developing new microfluidic tools for various biomedical applications. For example, we use real-time image analysis to identify droplets with different encapsulations and perform downstream droplet manipulations. We develop new technologies to pattern antibodies with high resolutions and multiplexity.
Relevant Publications:
- High resolution, multiplex antibody patterning using micropillar-focused droplet printing and microcontact printing
Meichi Jin, Kai Wu, Mengzhen Wang, Yang Zhang, Chengbin Yang, and Zida Li*
Advanced Biology
, in press
DOI | PDF - Syringe-pump-induced fluctuation in all-aqueous microfluidic system implications for flow rate accuracy
Zida Li, Sze Yi Mak, Alban Sauret, and Ho Cheung Shum*
Lab on a Chip
, 14(4), 744-749, 2014
DOI | PDF
English | 中文